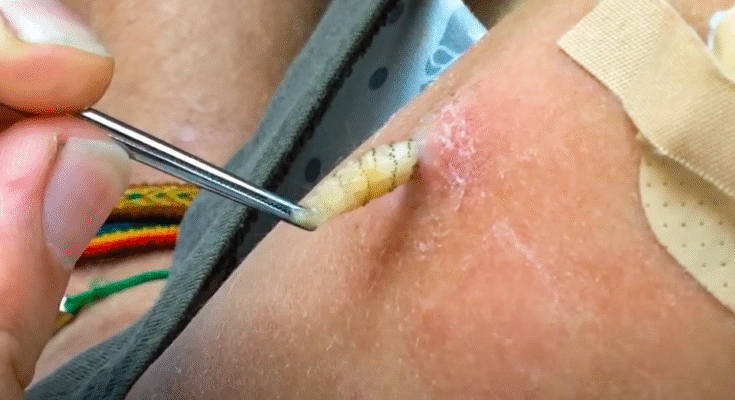
🔍 What is a Sebaceous Cyst?
A sebaceous cyst is a small, non-cancerous bump beneath the skin, typically filled with oily or cheesy material (sebum). They’re usually slow-growing and painless unless they become infected.
👀 Signs of a Sebaceous Cyst
-
A round bump under the skin (commonly on the face, neck, or torso)
-
A visible blackhead or central opening
-
Possible foul-smelling discharge
-
Redness, tenderness, or swelling (if infected)
🛠️ How to Treat a Sebaceous Cyst
🚫 Don’t:
-
Don’t squeeze or pop the cyst — this can cause infection or push contents deeper.
-
Don’t cut it yourself — it can lead to scarring or more serious infection.
✅ Do:
-
Leave it alone if it’s small, painless, and not infected.
-
Apply warm compresses to help it drain naturally (if it’s near the surface).
-
Keep the area clean and monitor for changes.
🩺 When to See a Doctor
Go to a doctor or dermatologist if:
-
It’s painful, red, or swollen (signs of infection)
-
It keeps coming back
-
It grows rapidly
-
You want it removed for cosmetic reasons
Doctors might:
-
Drain it (incision and drainage)
-
Inject it with steroids (to reduce inflammation)
-
Surgically remove the cyst wall (to prevent recurrence)
🩺 How a Sebaceous Cyst Is Removed
1. Minor Surgical Procedure (Excision)
-
Procedure: A doctor numbs the area with local anesthesia, makes a small cut, and removes the entire cyst including the sac (cyst wall).
-
Goal: Complete removal to prevent recurrence.
-
Time: Usually done in 20–30 minutes in a clinic or outpatient setting.
-
Recovery: Mild soreness for a few days, with a small scar possible.
2. Drainage (Not Always Recommended Alone)
-
If infected or swollen, the cyst might be lanced and drained, but this often doesn’t remove the cyst wall, so it may come back.
-
May be combined with antibiotics if there’s an infection.
3. Laser or Minimal-Incision Techniques (less common)
-
Used for cosmetic areas or minimal scarring, but only in select cases.
🧼 Aftercare
-
Keep the area clean and dry.
-
Watch for signs of infection (increased redness, swelling, pus).
-
Follow any instructions for dressing changes or follow-up.
⚠️ Do Not Attempt at Home
Removing a sebaceous cyst at home can cause:
-
Infection
-
Incomplete removal (it comes back)
-
Scarring
-
Pain or bleeding
🩺 Sebaceous Cyst Removal: Detailed Overview
🔬 What is a Sebaceous Cyst?
A sebaceous cyst, also known as an epidermoid cyst, is a benign, slow-growing lump beneath the skin filled with keratin. These cysts often develop when hair follicles become clogged or damaged. They are typically found on the face, neck, or torso but can occur anywhere on the body .
🛠️ Surgical Techniques for Removal
1. Wide Excision
-
Procedure: A larger incision is made around the cyst to remove it entirely, including the cyst wall.
-
Benefits: Minimizes the chance of recurrence.
-
Considerations: May result in a more noticeable scar .
2. Minimal Excision
-
Procedure: A small incision is made, and the cyst contents are expressed. The cyst wall is then removed through the same incision.
-
Benefits: Less invasive with minimal scarring.
-
Considerations: Higher risk of recurrence if the entire cyst wall isn’t removed .
3. Punch Excision
-
Procedure: A circular punch tool is used to remove the cyst and surrounding tissue.
-
Benefits: Quick and effective for small to medium-sized cysts.
-
Considerations: May require sutures; not suitable for very large cysts .
4. Laser-Assisted Excision
-
Procedure: A laser is used to drain the cyst contents, and the cyst wall is removed later.
-
Benefits: Minimizes scarring and is suitable for cosmetically sensitive areas.
-
Considerations: May require multiple sessions .
🧪 Pre-Surgical Preparation
Before the procedure:
-
Consultation: Discuss your medical history, allergies, and any medications you’re taking.
-
Imaging: In some cases, ultrasound or CT scans may be used to assess the cyst.
-
Consent: Sign an informed consent form acknowledging understanding of the procedure and potential risks .
🏥 During the Procedure
-
Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the area.
-
Incision: The chosen surgical technique is performed to remove the cyst.
-
Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or adhesive strips, depending on the technique used .
🩹 Post-Surgical Care
After the procedure:
-
Wound Care: Keep the area clean and dry. Follow your doctor’s instructions for dressing changes.
-
Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended.
-
Signs of Infection: Watch for increased redness, swelling, or discharge, which could indicate infection.
-
Follow-Up: Attend any scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor healing .
⚠️ Risks and Considerations
-
Recurrence: If the entire cyst wall isn’t removed, the cyst may return.
-
Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there’s a risk of infection.
-
Scarring: Depending on the surgical technique and location, scarring can occur .
✅ I can help you by:
-
Guiding you on what to expect before, during, and after treatment.
-
Helping you prepare questions for your doctor.
-
Finding a local clinic or provider if you need one.
-
Explaining home care safely while waiting for treatment (if it’s not infected).
⚕️ What You Should Do Next
To get a sebaceous cyst safely removed, please:
-
📅 Schedule an appointment with a:
-
Dermatologist
-
General surgeon
-
Primary care physician
-
-
🔍 Mention you have a “sebaceous cyst and would like it evaluated for removal.”
Would you like me to:
-
Help you find a clinic near you?
-
Help you write a message or script to ask your doctor about it?
-
Go over home care tips while waiting?