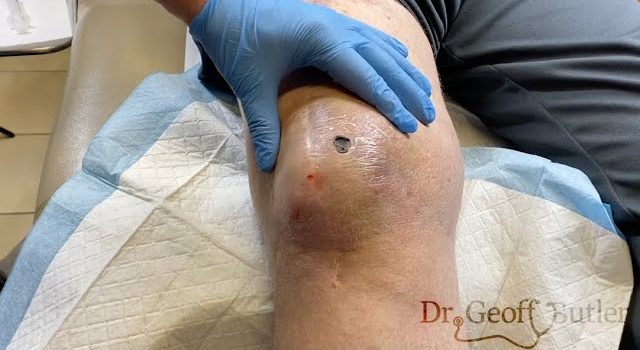
Knee hematomas, which occur when blood accumulates in the tissues around the knee joint due to injury, can cause significant discomfort, swelling, and limited mobility. Effective drainage of a knee hematoma is crucial in facilitating faster recovery and reducing the risk of complications. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to effectively drain a knee hematoma and ensure optimal healing.
The first step in managing a knee hematoma is to properly assess the extent of the injury. Mild hematomas may resolve with conservative treatments, such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E.). However, more severe cases with significant swelling and pressure buildup may require professional intervention.
One common method of drainage is aspiration, where a healthcare provider uses a needle or syringe to remove the accumulated blood from the knee joint. This procedure is often done under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. Aspiration helps to relieve pressure, reduce swelling, and prevent complications like joint stiffness or infection.
In some cases, if the hematoma is large or recurrent, surgical drainage may be necessary. This involves making a small incision to allow the blood to drain more effectively. Surgeons may also examine the knee for any underlying damage that could be contributing to the hematoma.
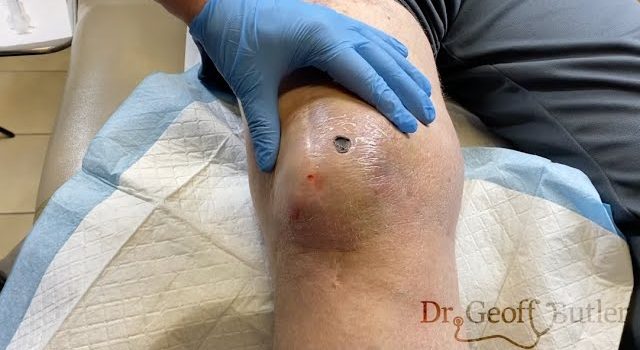
After drainage, rehabilitation becomes a critical part of the recovery process. Physical therapy exercises help restore movement and strength to the knee while preventing future injuries. During this time, patients should continue to follow a care plan that includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation to manage swelling.
In conclusion, draining a knee hematoma effectively requires timely intervention, appropriate medical procedures, and a careful rehabilitation plan. With the right approach, recovery can be faster, and the risk of long-term complications is minimized.
A knee hematoma refers to a collection of blood that accumulates around the knee joint due to trauma or injury, such as a fall or blow to the knee. Hematomas happen when blood vessels are damaged and blood leaks into the surrounding tissues, causing swelling and bruising. Here are the steps typically taken to manage a knee hematoma:
1. Rest
- Avoid putting weight on the injured knee to prevent further damage and reduce swelling. Using crutches may help if necessary.
2. Ice Therapy (Cold Compress)
- Apply an ice pack or cold compress to the affected area for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours during the first 48 hours. Cold helps reduce swelling, inflammation, and pain by constricting blood vessels.
3. Compression
- Use an elastic bandage or compression wrap around the knee to help control swelling. However, it shouldn’t be too tight, as this can affect circulation.
4. Elevation
- Elevate the knee above the level of your heart as much as possible to reduce swelling. Prop your leg up on pillows while resting.
5. Pain Management
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help with pain and swelling. Be cautious with NSAIDs (like ibuprofen), as they can increase bleeding.
6. Monitor for Severe Symptoms
- If you experience severe pain, difficulty moving the knee, or signs of a more serious injury (such as a fracture), it’s important to see a doctor. They might need to drain the blood if the hematoma is large or painful.
7. Physical Therapy (if needed)
- If the injury is more severe and mobility is affected, physical therapy may be recommended to help regain strength and mobility in the knee.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- The hematoma is unusually large or the swelling continues to worsen.
- You experience severe pain or difficulty moving the knee.
- There are signs of infection (redness, warmth, pus).
- You are unable to bear weight or walk on the leg.