Scroll Down to watch👇👇
Pimple Blackheads: Unmasking the Culprits of Skin Woes
Introduction
Pimple blackheads—those tiny, stubborn dots that seem to defy all skincare efforts—are a common annoyance for many. Whether they camp out on our noses, chins, or backs, blackheads can be perplexing. Let’s delve into their origins, appearance, and strategies for dealing with these pesky skin intruders.
Blackheads are a type of acne (acne vulgaris). Unlike their fiery cousins—the inflamed red pimples—blackheads appear as open bumps on the skin. Picture tiny dark specks dotting your T-zone or scattered across your back. But what causes them?
The Culprit: Clogged Pores
Blackheads emerge when hair follicles become clogged with excess oil (sebum) and dead skin cells. These clogs create a cozy environment for bacteria, leading to the formation of—you guessed it—blackheads. But why do they look black?
The Oxidation Effect
Contrary to popular belief, blackheads aren’t filled with dirt. Instead, an irregular reflection of light off the clogged follicle gives them their dark hue. When the material inside the pore is exposed to air, it oxidizes, turning the blackhead black. So, it’s not dirt—it’s science!
Treatment Strategies
Gentle Cleansing: Regularly cleanse your skin with a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser. This helps remove excess oil and dead skin cells, preventing blackheads from settling in.
Exfoliation: Exfoliating 2-3 times a week with products containing salicylic acid or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) helps keep pores clear and reduces blackhead formation.
Topical Treatments: Look for products with ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or retinoids. These help unclog pores and regulate oil production.
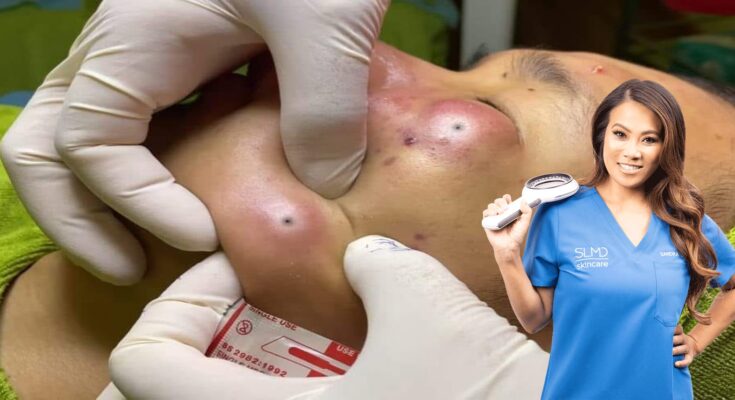
Professional Extraction: For stubborn blackheads, consider professional extraction by a dermatologist. They’ll ensure complete removal without damaging your skin.
Popping pimples and blackheads isn’t generally recommended because it can lead to scarring, infection, or even cause more breakouts. However, if you still want to tackle blackheads or pimples carefully, here’s how you can do it safely:
For Pimples (Whiteheads or Pimples):
- Wash Your Hands: Start by washing your hands thoroughly to avoid transferring bacteria.
- Clean Your Skin: Gently cleanse your face with a mild facial cleanser to remove dirt and oil.
- Steam Your Face: Use steam to open up your pores. You can either take a hot shower or hold your face over a bowl of hot water with a towel over your head (like a mini sauna) for 5-10 minutes.
- Use a Comedone Extractor: If the pimple is ready to pop (white and not inflamed), use a clean comedone extractor (a small metal tool) to gently press on either side of the pimple.
- Apply a Spot Treatment: After popping, apply an antibacterial ointment or acne spot treatment to reduce the risk of infection.
For Blackheads:
- Exfoliate: Gently exfoliate your skin to remove dead skin cells. You can use a mild scrub or a chemical exfoliant like salicylic acid.
- Apply a Blackhead Remover Strip: These strips are designed to help pull out blackheads, but be gentle and follow the instructions.
- Use a Blackhead Extractor: After steaming your face, gently press around the blackhead with a blackhead extractor tool. Do not force it.
- Apply a Toner: After removing blackheads, use a toner with ingredients like witch hazel or salicylic acid to close your pores.
Key Tips:
- Don’t Squeeze With Your Fingers: This can introduce bacteria, making the problem worse and possibly leading to scarring.
- Avoid Overdoing It: Too much squeezing or picking can irritate the skin, leading to more breakouts.
- Moisturize: Always moisturize after treating your skin to prevent it from drying out.
How to Safely Pop Pimples (Whiteheads)
Popping pimples can increase the risk of scarring or infection, so it’s essential to follow the proper steps to minimize these risks.
1. Start by Cleaning Your Hands
- Why? Hands carry bacteria, which can cause further infections when touching your face. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water to remove any germs.
- Reference: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advises frequent hand washing to prevent the spread of bacteria.
2. Cleanse Your Skin
- Use a mild facial cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup from your skin. Avoid harsh cleansers that strip away natural oils, as they can irritate your skin.
- Best Practices: Use a gentle, non-comedogenic (won’t clog pores) cleanser, such as Cetaphil Daily Facial Cleanser or La Roche-Posay Toleriane Hydrating Gentle Cleanser.
- Reference: American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) recommends using gentle skincare products for acne-prone skin to prevent irritation.
3. Steam Your Face
- Why? Steaming your face helps to open pores and softens the skin, making it easier to extract pimples and blackheads.
- You can do this by taking a hot shower or holding your face over a bowl of hot water with a towel draped over your head.
- Steam for: About 5-10 minutes.
- Reference: AAD advises using steam to help clear the pores in acne-prone skin.
4. Use a Comedone Extractor Tool (Optional)
- Why? This tool applies gentle pressure to extract the pimple’s contents without causing injury to the surrounding skin.
- If you’re dealing with a whitehead, you can use a sterile comedone extractor. Make sure to clean the tool with rubbing alcohol before use.
- Apply gentle pressure around the pimple, not directly on it. You may want to move the tool in a circular motion.
- Reference: Dermatology Times suggests using sterile tools like comedone extractors to avoid introducing bacteria.
5. Aftercare
- Antibacterial Ointment: After extracting the pimple, use an antibacterial ointment (like Neosporin) to reduce the risk of infection.
- Spot Treatment: Apply a targeted acne treatment containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid to reduce inflammation.
- Reference: AAD recommends using spot treatments containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid for active acne lesions.
How to Remove Blackheads
Blackheads form when pores become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. Unlike pimples, they remain open at the surface, which is why they appear black. Here’s how to remove them safely:
1. Exfoliate Your Skin
- Exfoliating removes dead skin cells, preventing them from mixing with sebum (oil) to clog pores.
- Use a gentle scrub or, for more effective exfoliation, a chemical exfoliant containing salicylic acid (a beta hydroxy acid, or BHA) that can penetrate pores.
- Recommended Exfoliant: Paula’s Choice Skin Perfecting 2% BHA Liquid Exfoliant or Neutrogena Oil-Free Acne Wash with Salicylic Acid.
- Reference: AAD recommends using salicylic acid-based products to exfoliate and prevent acne.
2. Apply Blackhead Remover Strips (Optional)
- How They Work: These strips adhere to the blackheads and pull them out when removed.
- How to Use: Apply the strips after cleansing and steaming your face. Let them sit for a few minutes before gently removing them.
- Recommended Strips: Biore Deep Cleansing Pore Strips.
- Reference: Dermatology Review suggests that pore strips can help remove superficial blackheads but advises caution because they can also irritate sensitive skin.
3. Use a Blackhead Extractor Tool
- Why? If a blackhead hasn’t come out with a pore strip, a blackhead extractor tool can help.
- Apply light pressure on either side of the blackhead to release the plug. Avoid using excessive force.
- Clean the tool: Sterilize it with alcohol before and after use.
- Reference: American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) suggests using tools like blackhead extractors for safe and effective extractions.
4. Aftercare
- Toner: After removing blackheads, use a gentle toner with ingredients like witch hazel or salicylic acid to tighten pores.
- Moisturize: Even though you’re focusing on blackheads, keep your skin hydrated to prevent dryness and irritation.
- Recommended Toner: Thayers Witch Hazel Toner, or Paula’s Choice Skin Recovery Calming Toner.
- Reference: AAD recommends toners with salicylic acid to close pores and prevent new blackheads from forming.
General Advice for Treating Pimples and Blackheads
- Don’t Squeeze With Your Fingers: Squeezing pimples with your fingers can transfer bacteria and cause the pimple to worsen.
- Avoid Over-Extraction: Extracting too frequently can irritate your skin and lead to new breakouts.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If you have persistent acne, a dermatologist can provide professional extractions and suggest prescription treatments.
Solutions for Pimples (Acne)
Home Solutions
-
Topical Acne Treatments
-
Benzoyl Peroxide: It helps to kill acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation. Apply a 2.5% or 5% gel or cream directly to the affected area.
- Recommended Product: Clean & Clear Persa Gel 10 (10% Benzoyl Peroxide) or Neutrogena On-the-Spot Acne Treatment.
- Reference: American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) suggests that benzoyl peroxide can help reduce acne inflammation.
-
Salicylic Acid: A BHA that penetrates deep into pores, exfoliating dead skin cells and unclogging pores, making it effective for blackheads and pimples.
- Recommended Product: Paula’s Choice Skin Perfecting 2% BHA Liquid Exfoliant or Neutrogena Oil-Free Acne Wash.
- Reference: AAD and Mayo Clinic recommend salicylic acid for treating mild to moderate acne by preventing clogged pores.
-
-
Tea Tree Oil
- Tea tree oil has natural antimicrobial properties that can help kill bacteria causing acne and reduce inflammation.
- How to Use: Dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil (like jojoba or coconut oil) and apply a drop to the pimple.
- Recommended Product: The Body Shop Tea Tree Oil.
- Reference: Australian Journal of Dermatology (2007) found tea tree oil to be effective in treating acne, reducing the severity of pimples.
-
Aloe Vera
- Aloe vera has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce redness and irritation, helping pimples heal faster.
- How to Use: Apply pure aloe vera gel directly to the pimple as a natural treatment.
- Recommended Product: Fresh Aloe Vera Gel or Amara Organics Aloe Vera Gel.
- Reference: Mayo Clinic recommends aloe vera for its skin healing and anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Retinoids
- Retinoids, such as retinol or adapalene, are powerful at unclogging pores, speeding up cell turnover, and preventing new breakouts.
- Recommended Product: Differin Gel (Adapalene 0.1%), available over-the-counter.
- Reference: AAD advises the use of retinoids for preventing acne, especially for individuals with persistent breakouts.
-
Ice for Inflammation
- Applying ice can reduce swelling and redness of an inflamed pimple, especially when it’s painful or large.
- How to Use: Wrap an ice cube in a clean cloth and gently press it on the pimple for 1-2 minutes.
- Reference: This method is often recommended by dermatologists for reducing swelling and discomfort temporarily.
Professional Solutions
-
Topical or Oral Antibiotics
- If over-the-counter treatments aren’t effective, dermatologists may prescribe oral antibiotics (like doxycycline or minocycline) or topical antibiotics (like clindamycin) to fight the bacteria causing acne.
- Reference: AAD and American Academy of Dermatology suggest using antibiotics for more severe cases of acne or when topical treatments aren’t enough.
-
Chemical Peels
- A chemical peel uses acids (like salicylic acid or glycolic acid) to exfoliate the skin, improve cell turnover, and reduce acne.
- Professional Treatment: A dermatologist or licensed aesthetician will apply the peel in-office for best results.
- Reference: American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) supports chemical peels as an effective treatment for acne.
-
Laser Treatments
- Certain laser treatments, such as blue light therapy, target the bacteria in the skin causing acne and can reduce the size of sebaceous (oil) glands.
- Recommended Treatment: Laser acne treatment, which can be done by a dermatologist.
- Reference: AAD reports that light-based therapies, including lasers, are effective at treating acne and reducing scarring.
Solutions for Blackheads
Home Solutions
-
Salicylic Acid-based Products
- As a BHA, salicylic acid is one of the most effective ways to treat blackheads by breaking down the oils and dead skin that clog pores.
- Recommended Product: Paula’s Choice Skin Perfecting 2% BHA Liquid Exfoliant or Neutrogena Oil-Free Acne Wash.
- Reference: AAD recommends salicylic acid for preventing blackheads and keeping pores clear.
-
Retinoids
- Retinoids also help with blackheads by increasing cell turnover, which helps clear pores and prevent the formation of comedones.
- Recommended Product: Differin Gel (Adapalene 0.1%).
- Reference: AAD states that retinoids can effectively treat blackheads and acne.
-
Clay Masks
- Clay masks, especially those with bentonite or kaolin clay, help to absorb excess oil, draw out impurities, and reduce blackheads.
- Recommended Product: Aztec Secret Indian Healing Clay (mix with apple cider vinegar) or Innisfree Super Volcanic Pore Clay Mask.
- Reference: AAD recommends clay masks for absorbing excess oils, which help prevent and treat blackheads.
-
Pore Strips
- Pore strips can help temporarily remove blackheads by adhering to the oils and impurities in your pores.
- Recommended Product: Biore Deep Cleansing Pore Strips.
- Reference: Although pore strips can help remove surface-level blackheads, AAD advises caution, as they can sometimes irritate the skin.
Professional Solutions
-
Facials or Manual Extractions
- A professional facial at a dermatologist’s office or spa can target blackheads. A licensed aesthetician will carefully extract blackheads using sterile tools, minimizing the risk of scarring.
- Reference: AAD recommends facials with extractions for individuals who struggle with persistent blackheads.
-
Microdermabrasion
- This treatment involves using tiny exfoliating crystals to remove dead skin cells and promote the renewal of fresh skin. It can help with blackheads by reducing pore clogging.
- Recommended Treatment: Microdermabrasion performed by a dermatologist or licensed esthetician.
- Reference: American Society for Dermatologic Surgery suggests microdermabrasion to treat blackheads and overall skin texture.
-
Laser and Light-Based Treatments
- Laser therapy, like Fractional CO2 laser or blue light therapy, can help to reduce oil production, kill acne-causing bacteria, and shrink the size of pores.
- Recommended Treatment: Consult with a dermatologist for specific laser treatments targeted at reducing blackheads and acne.
- Reference: AAD and Dermatology Times mention that laser treatments can significantly reduce blackheads over time.
Additional Treatment Considerations
- Diet: While the connection between diet and acne is still debated, some studies suggest that high-glycemic foods (like sugary snacks and refined carbs) and dairy might exacerbate acne. Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can support skin health.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help maintain skin hydration and flush out toxins.
- Sun Protection: Always apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily (even if you’re using acne treatments), as some treatments can make your skin more sensitive to the sun. Recommended Product: EltaMD UV Clear Broad-Spectrum SPF 46.
Final Advice:
- Consistency: Treating acne and blackheads requires patience. Give any solution you try at least 4-6 weeks to show results.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If over-the-counter treatments aren’t working, or your acne is severe, a dermatologist can help you develop a treatment plan tailored to your skin’s needs.