Scroll Down to watch👇👇
How do you diagnose a sebaceous cyst?
A diagnosis of a sebaceous cyst can be determined by a physical examination of the nodule by a dermatologist, family physician or other healthcare provider. There are occasions when additional testing is required to make a definitive diagnosis of a cyst, since it can sometimes be mistaken for a different type of skin tumor.
Common tests used to diagnosis a sebaceous cyst include:
- Cat scan – This test is performed to rule out other abnormalities or cancer.
- Ultrasound – This test is performed to establish the contents of the cyst and depth of inflammation.
- Punch biopsy – This test is performed to identify the histology of the cyst.
- Culture and Sensitivity – This exam is performed to determine the type of bacteria responsible for the infection and the best antibiotic to treat the infection.
What is the best treatment for a sebaceous cyst?
Depending on the size of the sebaceous cyst, there are many different options for treatment. The cyst may need to be surgically excised or drained depending on the severity of the cyst. In dermatology, most cysts that are removed are done so because of their cosmetic appearance or because of discomfort. A board certified dermatologist, like Dr. Green in NYC, will discuss the best treatment available to remove your cyst, based upon her clinical evaluation. Some sebaceous cysts which are quite large or on the face, may require a plastic surgery for cyst removal. The treatment options for cyst removal depends on the anatomic location of the cyst, its size, and whether or not the cyst is already infected. Dr. Green will guide your treatment to provide the best aesthetic as well as medical outcome.
A sebaceous cyst is usually diagnosed through a physical examination by a healthcare provider. Here’s how it generally works:
- Medical History: The doctor may ask about the history of the cyst, including how long you’ve had it, whether it has changed in size, and if you’ve noticed any pain or drainage from the cyst.
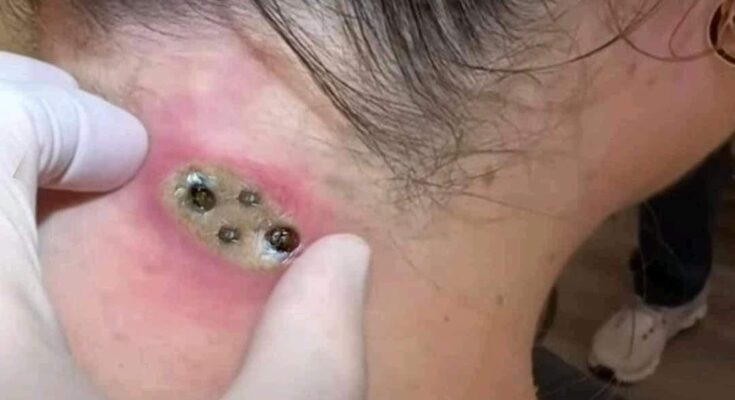
- Visual and Physical Exam: The doctor will examine the cyst to assess its size, shape, and location. Sebaceous cysts are typically round, firm, and movable under the skin. They often have a central pore or opening, through which the contents may drain.
- Palpation: The doctor may gently press on the cyst to assess its consistency and whether there is any tenderness or signs of infection (such as redness, warmth, or swelling).
- Imaging (in some cases): If the diagnosis is unclear, or if there’s a concern that the growth could be something else, imaging techniques like an ultrasound or MRI may be used to confirm the diagnosis and check if there are any complications.
- Biopsy (rarely needed): If there’s a concern that the growth might not be a sebaceous cyst (for example, if it’s large, painful, or growing rapidly), a biopsy might be done to rule out other conditions like a tumor or abscess.
Most of the time, a sebaceous cyst can be diagnosed based on its appearance and characteristics. If the cyst becomes infected or problematic, medical intervention may be needed for drainage or removal.