What Causes Blackheads?Blackheads, also known as open comedones, form when dead skin cells, sebum, and bacteria become trapped in a hair follicle. This is due to a clogged pore that doesn’t let the skin cell and oil debris escape. As a result, a blackhead forms. They can appear on the nose, chin, forehead, chest, and other areas of the body. To prevent blackheads from forming, it’s important to regularly wash your face with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt and oils. Exfoliating two to three times per week can also help to keep pores unclogged and avoid the buildup of dead skin cells. However, if blackheads do form, there are ways to treat them. One method is popping or squeezing the blackheads. Dr. Fua can incorporate all of these treatment options into your acne treatment plan, depending on what works for your skin.
If topical treatment alone does not improve acne, or if acne is severe or extensive, oral medications are the best option. If you’ve tried several topical medications without success, or if your condition is severe, oral acne medications are usually the next step in the treatment process. Treatment usually includes oral antibiotics and applying a prescription gel or topical cream to the skin. Depending on people with acne, treatment may include using prescription creams to prevent acne, taking antibiotics to kill bacteria that contribute to acne, or, if acne is severe, taking stronger medications such as like isotretinoin, or even minor surgery. Even if you have tried topical acne treatments such as creams or gels without any lasting results, laser therapy may be the right solution for you. While I would like you to try natural remedies first, if you are not seeing improvement and severe hormonal acne is making your quality of life worse, other treatments can make a real difference. While it may take a while, treating hormonal acne from the inside out until your hormones are in their natural, happy balance will allow your skin to truly heal.
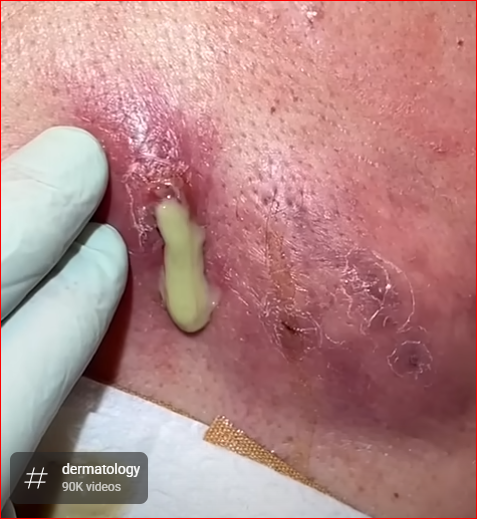
Treating a painful, large abscess requires a combination of medical drainage, pain management, infection control, and wound care. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how healthcare professionals typically treat it:
🔍 What Is an Abscess?
An abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection. Large and painful abscesses are often filled with infected fluid and dead tissue, and cannot heal without intervention.
🚨 When to Seek Medical Care
You should seek immediate medical attention if:
-
The abscess is large or growing quickly
-
You have fever, chills, or feel unwell (systemic symptoms)
-
The area is red, warm, swollen, and extremely painful
-
You have a weakened immune system or diabetes
-
The abscess is on the face, spine, or near the anus/genitals
✅ Step-by-Step Treatment for a Painful Large Abscess
1. Medical Evaluation
-
A doctor will assess the size, depth, and location.
-
Ultrasound may be used to detect the extent or confirm fluid buildup.
2. Incision and Drainage (I&D) – Main Treatment
Performed in a clinic, urgent care, or ER.
🔪 Procedure:
-
Local anesthesia is given to numb the area.
-
A sterile scalpel is used to make a small cut in the abscess.
-
Pus is drained completely.
-
Irrigation with saline to clean the inside.
-
Packing (gauze) may be placed to keep the wound open for continued drainage.
📌 Reference:
3. Antibiotics – If Infection Is Spreading or High-Risk
-
Prescribed when:
-
The abscess is large or deep
-
You have fever or cellulitis
-
The abscess is on the face
-
You are immunocompromised
-
Examples:
-
Clindamycin
-
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim)
-
Doxycycline
📌 Reference:
4. Pain Management
-
NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) or acetaminophen are commonly used.
-
For severe cases, short-term prescription pain relief may be provided.
5. Wound Care at Home
-
Keep the area clean and dry
-
Change dressings daily or as instructed
-
Follow up with your provider to remove packing (if used)
-
Monitor for signs of recurrence or spreading
6. Possible Complications if Left Untreated
-
Spreading infection (cellulitis, sepsis)
-
Formation of fistulas or chronic wounds
-
Need for surgical intervention
📌 Summary
| Step | Treatment |
|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | See a doctor immediately |
| 2️⃣ | Abscess drainage (I&D) |
| 3️⃣ | Antibiotics if needed |
| 4️⃣ | Pain relief (NSAIDs or stronger if necessary) |
| 5️⃣ | Wound care and follow-up |