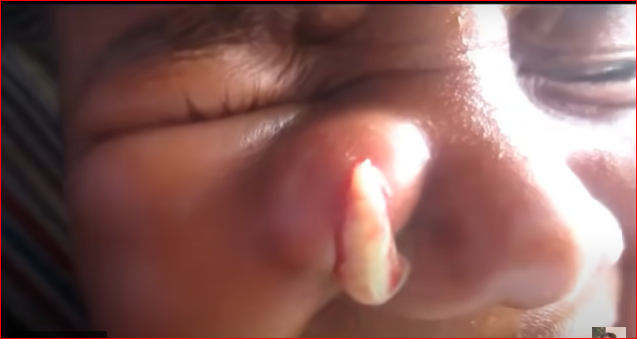
An abscess on the side of your nose can occur when bacteria enter a hair follicle or a sweat gland, causing infection and inflammation. Here’s how it typically forms:
-
Infection: The skin near your nose can be prone to bacterial infections, especially if it’s exposed to dirt, oils, or other contaminants. The bacteria can enter the skin through a small break or cut, or by clogging pores.
-
Blocked Pores or Follicles: If a pore or hair follicle near the nose becomes clogged with oil, dead skin cells, or other debris, it can become inflamed and infected, eventually forming an abscess.
-
Ingrown Hairs: Sometimes, an ingrown hair can cause a localized infection, leading to an abscess.
-
Poor Hygiene or Touching the Area: If you frequently touch your face, particularly the side of the nose, without washing your hands, it increases the risk of transferring bacteria.
Treatment Options:
- Warm Compress: Apply a warm, moist cloth to the abscess for 15–20 minutes several times a day to help it drain and relieve discomfort.
- Antibiotics: If the abscess becomes infected, a doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics or topical treatments.
- Drainage: If the abscess doesn’t drain on its own, a healthcare provider may need to drain it using sterile techniques.
- Avoid Popping: Never attempt to squeeze or pop an abscess yourself, as this can worsen the infection and spread bacteria.
Causes:
-
Bacterial Infections: The most common cause is a bacterial infection, often by Staphylococcus aureus. These bacteria can enter the skin through minor cuts, abrasions, or hair follicles, leading to an abscess.
-
Nasal Vestibulitis: This is an infection of the nasal vestibule, the area just inside the nostrils. It can result from nose picking, excessive blowing, or other forms of trauma, leading to redness, swelling, and tenderness around the nostrils.
-
Folliculitis: Infection of the hair follicles near the nose can cause small, painful bumps that may develop into abscesses. This condition is often due to bacterial invasion of the hair follicles.
-
Nasal Furunculosis: A deeper infection of the nasal vestibule, often caused by Staphylococcus aureus, leading to the formation of boils inside the nostrils. This condition can cause significant discomfort and requires medical attention.
Symptoms:
-
Redness and swelling on the side of the nose.
-
Pain or tenderness in the affected area.
-
Warmth over the swollen area.
-
Possible pus drainage if the abscess ruptures.
Treatment:
-
Warm Compresses: Applying a warm, moist cloth to the affected area several times a day can help promote drainage and alleviate discomfort.
-
Antibiotics: If the abscess is large, persistent, or accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever, a healthcare provider may prescribe oral antibiotics to combat the infection.
-
Incision and Drainage: For larger abscesses, a doctor may perform a minor surgical procedure to drain the pus, relieving pressure and promoting healing. This is typically done under local anesthesia.
-
Avoid Squeezing: It’s crucial not to attempt to squeeze or pop the abscess, as this can worsen the infection and lead to complications.
Prevention:
-
Maintain good facial hygiene by washing the face regularly with mild soap and water.
-
Avoid touching or picking the nose to reduce the risk of introducing bacteria.
-
Keep any cuts or abrasions on the face clean and covered to prevent infection.